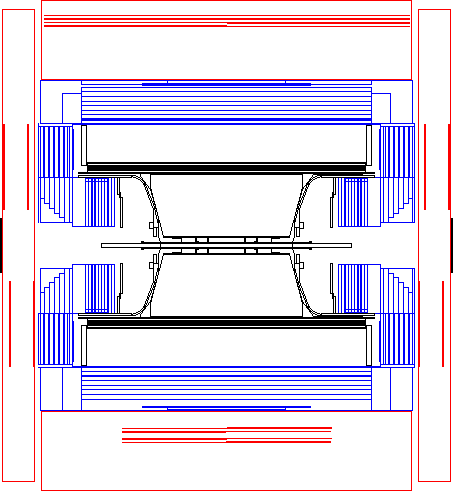

The hadron calorimeter measures the energy of hadrons emerging from the electromagnetic calorimeter and assists in the identification of muons. The iron of the magnet return yoke provides 4 or more interaction lengths of absorber over a solid angle of 97% of 4-pi. The yoke is segmented into layers, with planes of detectors between each layer, and forms a cylindrical sampling calorimeter about one meter thick.
To acheive coverage in solid angle, the hadron calorimeter is constructed in three parts:
The muon detector is constructed as a barrel and two endcaps and covers the iron yoke almost completely. While muons penetrate to the muon detector and leave a single clean track, most hadrons are absorbed the yoke. Information about the OPAL detector
Information about the OPAL detector
 Information about the electromagnetic calorimetry
Information about the electromagnetic calorimetry
 Information about the luminosity monitors
Information about the luminosity monitors